自2014年在意大利布林迪西举行第一届维和技术伙伴关系国际研讨会以来,已经启动了可行和可实施的项目。这些举措包括利用现有资源实现小规模但高影响力成果的速效项目,以及着眼于利用成员国的能力、技术和专门知识来提高外地行动特定领域的效力、效率、灵活性和反应能力的战略合作项目。联合国与成员国之间现有的伙伴关系继续蓬勃发展:奥地利、加拿大、丹麦、法国、德国、以色列、意大利、日本、卢森堡、荷兰、韩国、瑞士、英国和美利坚合众国。

Initiatives
Telemedicine Project
Partners: Australia, Germany, Ghana, Israel, Nepal, Japan, Portugal, Republic of Korea, United Nations Peace and Development Fund (UNPDF)
Status: Current
The United Nations prioritizes the health and well-being of personnel operating in diverse and remote settings where access to medical care is essential for mission success. Digital health technologies present an opportunity to enhance medical support systems, particularly in areas with strained or inaccessible services.
Initiated under the Triangular Partnership Programme (TPP) in 2021, the Telemedicine Project started as a pilot in four missions and has since expanded to over 30 sites across eight missions and two external Level 4 referral hospitals in Member States. Telemedicine Project won the 2023 Secretary-General Award in the category of innovation, digital, data and technology for the impact and transformative potential to healthcare delivery in remote areas.
Telemedicine supports various use cases, including real-time remote specialist guidance to stabilize trauma or complex cases at points of incident or deep field locations. It ensures secure transmission of medical information during evacuations and enables medical specialists to collaborate with in-mission teams, facilitating timely, life and limb-saving treatments for UN personnel in some of the world’s most hard-to-reach and challenging environments.
This initiative aligns directly with the UN’s vision of transforming into an agile and data-driven organization, as well as with the Peacekeeping Digital Transformation Strategy and the Secretary-General’s Information and Communications Technology Strategy. By leveraging innovative technologies, enhancing data ecosystems, and advancing enterprise infrastructure, telemedicine significantly contributes to enabling efficiencies and improvements in operations, supporting the Secretary-General’s UN80 Initiative.
To learn more, contact telemedicine@un.org.

Initiatives | Projects | Provision of Experts | Partnership Opportunities
方案
乌干达恩德培联合国C4ISR和平行动学院
合作伙伴:加拿大、丹麦、日本、乌干达、法国、北约
状态:持续进行
联合国C4ISR和平行动学院(UNCAP)致力于为维和人员在联合国旗帜下的角色做好准备。它旨在加强维和人员的行动准备和使用联合国指挥、控制、通信和计算机关键技术(C4);情报-监视-侦察(ISR);以及营地安全方面的表现。
UN Open GIS (Geospatial Information Systems) Initiative
Partners: Finland, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, United States of America
Status: Ongoing
The UN Open GIS Initiative, established in 2016, is an ongoing partnership initiative and supported by Member States, International Organizations including UN Agencies, Academia, NGOs, and the Private Sector.
The aim of UN Open GIS is the creation of an extended spatial data infrastructure by utilizing open source GIS solutions that meet the operational requirements of the United Nations (UN Secretariat including UN field missions and regional commissions). The initiative also reaches to UN agencies and operating partners, and to developing countries.
The UN Open GIS Initiative intends to provide a sustainable, hybrid GIS platform (integrating open source software GIS technology with the existing proprietary GIS platform) to effectively and efficiently support enhanced Situational Awareness and to inform decision-making. This will fulfill UN core mandates that refers to or depends on the following: geospatial information, the saving of lives and the support to emergency operations, and the enablement of cost-effective operations.
Various open source GIS solutions have been explored/assessed in the UN field operational environment, with findings of positive outcomes to move forward from the existing proprietary GIS platform toward the hybrid GIS platform. This is particularly on mobile GIS solutions (QField, KoBoToolbox, Geopaparazzi), desktop GIS solution (QGIS), OpenDroneMap, Cloud Free Satellite Imagery, and Hybrid GIS infrastructure.
To learn more, visit https://www.un.org/geospatial
ccc4545454545
项目
马里稳定团(联合国马里多层面综合稳定特派团)的马里稳定团特派团安全网络(MMSN)
合作伙伴:法国、荷兰、英国、意大利
状态:进行中
2016年1月至2017年2月,荷兰王国政府利用马里稳定团的TITAAN安全网络,提供了威胁评估支持服务——所有来源信息融合单位(ASIFU)。它于2017年2月28日正式退役。荷兰王国资助向马里稳定团特派团安全网络(MMSN)迁移数据,该网络由法国政府提供。
MMSN为特派团维和情报界的安全网络协作提供了一个平台。它用于处理、分析和分享通过各种来源(军事情报、政治、经济、社会和其他)收集的信息,这些来源相互协作,使特派团领导层能够更好地了解行动领域的现实情况。马里稳定团利用这些信息提供可预测和可操作的情报,以支持其活动。通过法国政府和联合国之间的协助函提供专门知识和网络服务。
在马里稳定团(联合国马里多层面综合稳定特派团)提供营地保护服务
合作伙伴:法国
状态:进行中
马里稳定团基达尔营地容易受到外部威胁,例如来自迫击炮弹炮击和火箭等来源的间接火力,以及营地附近发现的改进型爆炸装置。还查明了对人员的严重威胁,例如,吸附在联合国车辆下的磁性地雷。
该项目通过协助函建立,旨在加强基达尔营地的安全和保护水平,通过部署和全面管理专用设备的运维,将威胁暴露降至最低。这包括日间/夜间传感器(摄像头和雷达)、带两个高清远程摄像头的桅杆、移动桅杆上的摄像头和地面监视雷达。
马里稳定团高级威胁探测和传感器信息融合系统服务项目(联合国马里多层面综合稳定特派团)
合作伙伴:法国
状态:进行中
特派团所在地的威胁局势可能迅速恶化,已经发生了几起针对联合国人员和房舍的骚乱事件。有时,暴力升级到需要联合国营地警卫部队武装应对的程度。


cc545524434445
为协助特派团完成任务,该项目旨在为加奥营地提供更大的安全和保护,以加强现有措施。这包括部署和运行一个现代化的信息融合系统,该系统集成了昼夜传感器(摄像头和雷达),为传感器安装了一个45米的桅杆,并在加奥机场安装了传感器。该项目帮助联合国学习该技术,并为所有特派团制定综合营地安全和预警系统合同。
中非稳定团部队保护和安保技术处(联合国中非共和国多层面综合稳定特派团)
合作伙伴:以色列
状态:进行中
设立该项目是为了解决“远眺群山”的需要,以加强对特派团维和情报收集的支持,改善联合国维和人员营地安全、总体安全局势和态势感知质量。其目的是展示现代监控技术对检测不对称威胁的影响。
该项目为车队保护和其他行动需求提供威胁评估,以证明解决方案的技术潜力。它包括部署、运维多个战术无人机系统,这些系统可以在作战区的任何地方操作。专业知识、设备和服务是通过以色列政府和美国之间的协助函(LOA)提供的

Orbiter 3 Unmanned Aerial System used in MINUSCA
快速部署能力-模块化指挥中心项目
合作伙伴:德国
状态:进行中
通过模块化指挥中心(MCC)实现了在外地建立完全一体化通信网络的目标。这是一个基于海运集装箱的配置,由OICT设计,以支持外地特派团对可扩展、快速部署和可定制的移动通信中心的持续需求。MCC能够容纳最先进的设备。其设想是为一个指挥小组提供必要的工作环境,以便在无法提供永久基础设施的情况下进行指挥和控制,并将来自不同国家或联合国机构的军事特遣队使用的不同无线电系统连接到一个独特的波段基地,提供安全、可靠和有效的行动。最新一代提供了无线电、智能手机和计算机等多种不同通信设备之间的互操作性;并且它能够实现完全集成的通信网络,该通信网络可以由MCC操作员从部队中的舒适房间内控制。

Modular Command Centre and Modular Power Pack in Mayi Moya, MONUSCO
德国人道主义救济机构(德国联邦技术救援署,THW)在制定流程、培训和用户手册以及现场MCC的技术升级方面提供了额外的援助。五个MCC的资金由德国联邦政府提供。
马里稳定团(联合国马里多层面综合稳定特派团)无线电挖掘项目
合作伙伴:德国、荷兰
状态:进行中
联合国维和特派团越来越需要在敌对环境中行动,其特点是极端分子和民兵经常发动袭击。这些主要针对外地特派团的军事特遣队,但也针对文职人员。
该项目利用了联合国全球脉搏组织(UN Global Pulse)开发的大数据分析工具。预计该工具将提供额外的能力,使特派团能够采取必要的积极措施,在联合国实现可持续发展目标(SDG)的工作中提高维和态势意识。
由于马里约80%的人口使用无线电作为获取信息的主要来源,该工具将能够对公共广播节目中发表的匿名意见进行流式传播和分析,以提高洞察力。自动语音识别工具使用人工智能技术来突出感兴趣的主题,例如突发卫生事件或当地灾害。然后,分析师可以使用这些数据进行进一步分析。在这个阶段,项目正在为用户开发技术和定制工具,以测试可用性。
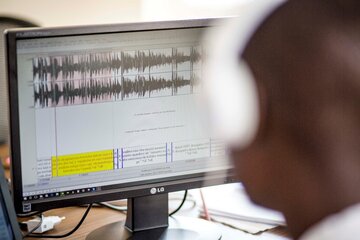
Data scientist in Pulse Lab Kampala working on speech-to-text technologies for indigenous languages. (Credit: @UNGlobalPulse)

Rapid Deployment Capabilities - the Modular Command Centre Project
Partner: Germany
Status: Current
The goal of a fully integrated communications network in the field has been realized through the Modular Command Centre (MCC). It is a sea container-based configuration designed by OICT to support the continuous needs of field missions for scalable, rapidly deployable and customizable mobile communications centre. MCCs are capable of hosting the most sophisticated equipment. It was conceived to provide the necessary work environment for a command group to exercise command and control where no permanent infrastructure can be provided, and to interconnect different radio systems in use by military contingents from different nations or UN agencies into a unique band base, providing safe, reliable and effective operations. The latest generation provides interoperability between a wide range of different communication devices such as radios, smartphones and computers; and it enables a fully integrated communication network that can be controlled by an MCC operator from a comfortable room within the unit.
The German Agency for Humanitarian Relief (Technisches Hilfswerk, THW), provides additional assistance in the development of processes, training and user manuals as well as with technical upgrades of the MCC in the field. The funding for five MCCs was provided by the Federal Government of Germany.

Radio Mining Project in MINUSMA (United Nations Multidimensional Integrated Stabilization Mission in Mali)
Partners: Germany, Netherlands
Status: Current
United Nations peacekeeping missions increasingly need to operate in hostile environments, characterized by frequent attacks that are executed by extremists and militias. These are directed primarily at the military contingents of the Field Missions but also at the civilian population.
The project utilizes a big data analytics tool developed by UN Global Pulse. The tool is anticipated to provide additional capabilities that will enable the mission to take the necessary pro-active measures for improved peacekeeping situational awareness in the United Nations efforts to meet the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
As around 80 per cent of the population in Mali uses radio as their main source for getting information, the tool will be able to stream and analyse anonymous opinions voiced on public radio programmes for greater insight. The automated speech recognition tool uses AI technology to highlight topics of interest, such as health emergencies or local disasters. Analysts can then use the data for further analysis. At this phase, the project is developing the technology and customizing tools for the user to test usability.
The UN Data Privacy and Protection Principles and the UNDG Guidance Note on Data Privacy, Protection, and Ethics guide the analysis and presentation of the results of this project.
This is a multidisciplinary project with the participation of the Office of Military Affairs of DPO, MINUSMA and OICT Business Relationship Management. For technical implementation, our partner is UN Global Pulse, the UN Secretary-General’s initiative on big data and AI.

cxc876545
《联合国数据隐私和保护原则》和《UNDG关于数据隐私、保护和道德操守的指导说明》指导本项目结果的分析和介绍。
《联合国数据隐私和保护原则》和《UNDG关于数据隐私、保护和道德操守的指导说明》指导本项目结果的分析和介绍
提供专家
根据伙伴关系项目的性质和所需的专业知识,参与的成员国也有机会参与其中,提供具有业务和技术背景的军事、警察或文职专家加入联合国现场项目小组。
迄今为止,成员国已将专家纳入这些举措:
中非稳定团营地中非稳定团营地保护技术项目
合作伙伴:以色列
状态:持续进行
联合国总部地理空间信息服务
合作伙伴:瑞士
状态:已完成
马里稳定团无线电挖掘和数据分析
合作伙伴:德国、荷兰
状态:持续进行
马里稳定团卫星通信服务
合作伙伴:卢森堡
状态:持续进行
联合国总部创新和保护技术
合作伙伴:加拿大
状态:已完成
马里稳定团安全网络和营地安全项目
合作伙伴:法国
状态:已完成
在联合国哥伦比亚特派团(UNMC)提供德国THW(德国联邦技术救援署)ICT专家服务
合作伙伴:德国
状态:已完成
保护技术项目
合作伙伴:以色列
状态:持续进行
联合国总部地理空间信息服务
合作伙伴:瑞士
状态:已完成
马里稳定团无线电挖掘和数据分析
合作伙伴:德国、荷兰
状态:持续进行
马里稳定团卫星通信服务
合作伙伴:卢森堡
状态:持续进行
联合国总部创新和保护技术
合作伙伴:加拿大
状态:已完成
马里稳定团安全网络和营地安全项目
合作伙伴:法国
状态:已完成
在联合国哥伦比亚特派团(UNMC)提供德国THW(德国联邦技术救援署)ICT专家服务
合作伙伴:德国
状态:已完成
THW机构的专门ICT人员快速部署ICT并提供服务,以满足联合国哥伦比亚特派团确定的紧急需求。(THW是民事保护领域的一个政府组织,在130多个国家提供了技术救济,并建立在专门人士自愿承诺的基础上)。
合作机会
伙伴关系是维和成功的基础。“三方伙伴关系”是联合国维和伙伴关系的一个特别富有成效的例子。开始标签结束标签开始标签结束标签在几个成员国的支持下,业务支助部 (DOS)和信息和通信技术厅(OICT)在维和技术伙伴关系倡议的框架下开展了广泛的技术合作。
支持可以采取多种形式:从预算外资金到实物捐助,如提供专家、导师或培训师和设备,支持维和技术方案或项目。
OICT每年在联合国DPO-DOS联合年度预算外资金请求框架内,向所有成员国常驻代表团提交一些与技术相关的项目提案。
OICT目前正在态势感知、地理空间情报(GEOINT)、微型无人机和反无人机、电磁谱管理、远程医疗、生态责任和智能技术、技术培训和能力建设等领域寻求成员国的支持。
有关维和技术伙伴关系倡议或伙伴关系机会的更多信息,请联系计划管理部门,邮箱:UN-PTP@un.org。
Partnership Opportunities
Partnerships are fundamental for peacekeeping success. “Triangular Partnerships” are a particularly fruitful example of partnerships in United Nations peacekeeping. With support from several Member States, the Department of Operational Support (DOS) and the Office of Information and Communications Technology (OICT) have carried out a wide range of technology partnerships under the umbrella of the Partnership for Technology in Peacekeeping initiative.
Support can take many forms: from extra-budgetary funding to in-kind contributions like provision of experts, mentors or trainers, and equipment in support of peacekeeping technology programmes or projects.
A number of technology-related project proposals are submitted by OICT on an annual basis to all the Permanent Missions of Member States within the framework of UN DPO-DOS joint annual extra-budgetary fund requests.
OICT is currently seeking the support from Member States in the areas of Situational Awareness, Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT), Micro-drones and Counter-drones, Electromagnetic Spectrum Management, Telemedicine, Eco-responsibility and SMART technologies, Technology Training and Capacity Building.
For more information about the Partnership for Technology in Peacekeeping initiative or partnership opportunities, please contact Programme Management at UN-PTP@un.org.